
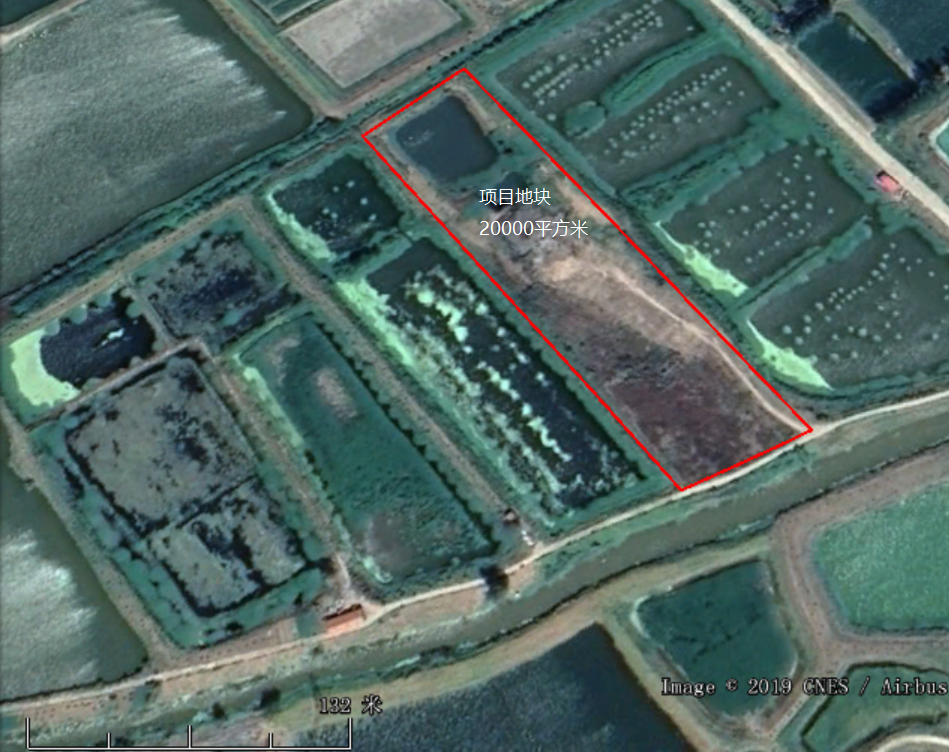
The project site is located in Longgan Lake Industrial Park, Huangmei County, Hubei Province, with a site area of about 20,000 square meters and an average landfill depth of about 6 meters. In order to solve the problem of domestic waste and general industrial solid waste disposal, Longgan Lake Management District has excavated a simple landfill in Longgan Lake Industrial Park since the 1980s. The original background of the landfill is an idle fish pond, and there are no protective measures around and at the bottom. The landfill was closed in 2008. Due to its long history, the type of garbage in the landfill is not yet clear, and about 1 meter of cover soil was filled on the landfill when it was closed. The geographic location is shown in Figure 1-1.
Figure 1-1 Schematic diagram of the geographical location of the project
Entrusted by the owner, it is now necessary to estimate the amount of waste under the landfill site, and to detect the boundary, depth, volume, the seepage of landfill leachate, and the status quo of the surrounding cultivated strata, and also need to find out whether the landfill leachate is mixed with groundwater, and migrates, and the dominant migration channel is identified. In the case of unknown conditions, in order to avoid secondary pollution caused by the spread of pollutants due to cleaning work in the later stage, it is necessary to use geophysical exploration methods under non-destructive and unexcavated conditions to find out the location and burial of landfills. In-depth basic information to prepare for the next construction work.

Induction electromagnetic method investigation
Since this survey is mainly to detect the landfill buried in the ground, after clarifying the site stratum information, a comprehensive induction electromagnetic (EM) survey is firstly conducted for the site area, and a conductivity distribution map within the site area is drawn for evaluation. There may be information such as the location and boundary of the landfill. This method is most suitable for a rapid and comprehensive census to detect the abnormal distribution range. It has the advantages of fast survey and high accuracy, especially for high conductivity and electrical conductivity compared with the formation. Anomalies of large differences.
High Density Resistivity Survey
After the EM detection is completed, the vertical actual depth of the abnormal area and the characteristics of the landfill are detected by the high-density resistivity method. The high-density resistivity survey aims to find out the depth and range of the buried landfill.
The high-density resistivity measurement line is carried out in the form of a single-sided grid measurement area, and the detection is planned based on the detection results of EM. The preliminary plan is to lay out 4 survey lines in the east-west direction, the line spacing is 30 meters, and the electrode spacing is 2 meters, each measuring line has 120 electrodes, with a guaranteed test depth of ≧ 10m; 9 north-south survey lines are used for rolling test, the line spacing is 30 meters, the electrode spacing is 1 meter, and each survey line has at least 60 electrodes. The specific ERT survey line is arranged as shown in Figure 2-2, and the on-site construction operation needs to be confirmed on site.
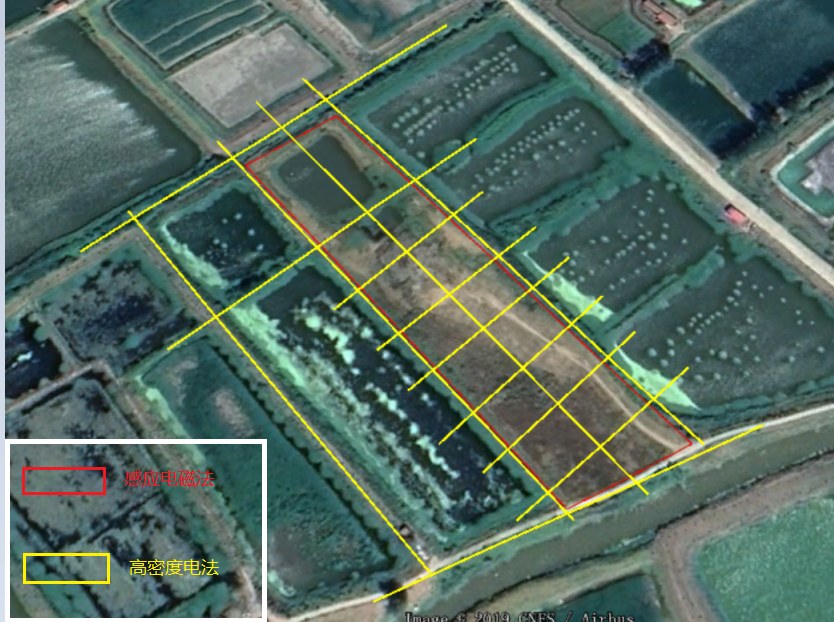
Figure 2-2 Layout of survey lines in the experimental site
The Electric Resistivity Method is also called the Direct Current Resistivity Method or the Geoelectric Resistivity Method. It is based on the difference of medium resistivity, observes the power supply current intensity and the potential difference between the measuring electrodes, and then calculates and studies the apparent resistivity, and infers the distribution of buried waste or possibly contaminated soil. The measured result is the ground resistivity profile. The factors affecting the formation resistivity are the constituent minerals, particle size, configuration, and the water content of the formation and the substances contained in the water. If the formation has obvious resistivity contrast, it is suitable for the DC resistance method.
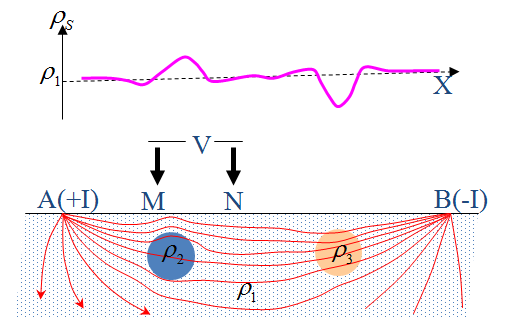
Figure 3-1 Schematic diagram of the principle of resistivity method
The high-density electrical method is the most widely used electrical survey developed from the resistivity method. Its basic theory is exactly the same as that of the traditional resistivity method, the difference is that the high-density electrical method sets a higher density of measuring points in the observation. When measuring on-site, all the electrodes only need to be arranged on the measuring points at a certain interval, and the mainframe&switch realy automatically controls the changes of the transmitting electrode and the receiving electrode. The high-density electrical measurement system adopts advanced automatic control theory and large-scale integrated circuits, and uses a large number of electrodes, and the electrodes can be freely combined, so that more geoelectric information can be extracted, so that electrical exploration can be like earthquakes. Exploration also uses multiple coverage measurements.
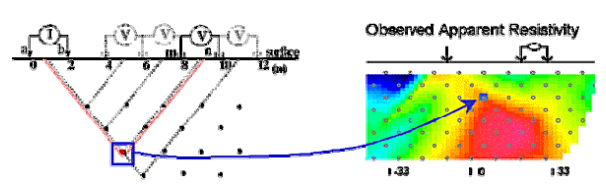
Figure 3-2 Schematic diagram of high density resistivity method
The high-density electrical method has the following advantages:
①The electrode layout is completed at one time, reducing the interference caused by the electrode setting and the measurement error caused by it; ②It can effectively carry out scanning measurement of various electrode arrangements, so that a richer geological information about structural characteristics of the geoelectric cross-section can be obtained;
③The field data collection is automated or semi-automated, which not only has a fast collection speed, but also avoids errors due to manual operations;
④On-site real-time processing and offline processing of data can be realized, which greatly improves the intelligence of the electrical method;
⑤ It can realize multi-parameter measurement, observe resistivity, polarizability and natural potential at the same time, obtain abundant underground geoelectric parameters, and describe underground structures from different electrical properties.
Electric method can be applied to the investigation of various types of sites, and can also obtain very rich results. When conducting a site survey, the abnormal resistivity should be determined by instruments first, and then confirm the standard resistivity value of the polluted abnormal site, select the standard electrical strata area where closest to the survey area and establish the standard electrical stratigraphic profile.
Principle of induction electromagnetic method
The induction electromagnetic method is mainly to obtain the characteristics of soil conductivity in a large range, and to delineate the distribution of the large conductivity of the site, which has a good effect on the delineation of the scope of heavy metal pollution.
Induction electromagnetic method, referred to as EM method, is to use the principle of electromagnetic induction to detect the formation. During the survey, the transmission coil is connected to a variable frequency alternating current (usually in the audio frequency range) on the surface to generate a primary magnetic field that changes with time. A time-varying eddy current is generated in the interior, and its current density depends on the resistivity of each layer. If the underground medium is not uniform, induced secondary magnetic fields will be generated on the overburden, surrounding rock and local conductors. The secondary magnetic field intensity is recorded by a receiving coil on the surface, which can be used to understand the electrical conductivity distribution of the underground stratum, and then infer the electrical structure and abnormal body of the stratum. The unit of physical quantity is often expressed in mS/m.
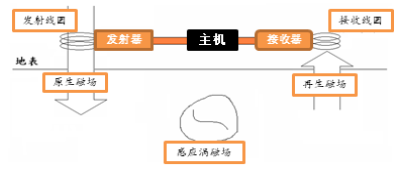
Figure 3-3 Schematic diagram of electromagnetic detection principle
Induction electromagnetic method can be used to understand the distribution of subsurface electrical properties in a large range of polluted sites. It is especially effective for site surveys with high conductivity. It is helpful for preliminary screening of abnormal landfill areas in the site, so as to facilitate the layout of subsequent geophysical exploration methods or the selection of the drilling sampling location. In recent years, the EM method has been applied to high-conductivity anomaly surveys. GPS is used for immediate positioning during surveying. Depending on site conditions, hundreds to hundreds of points can be performed every day. It can be used as a fast and effective tool for preliminary surveys.
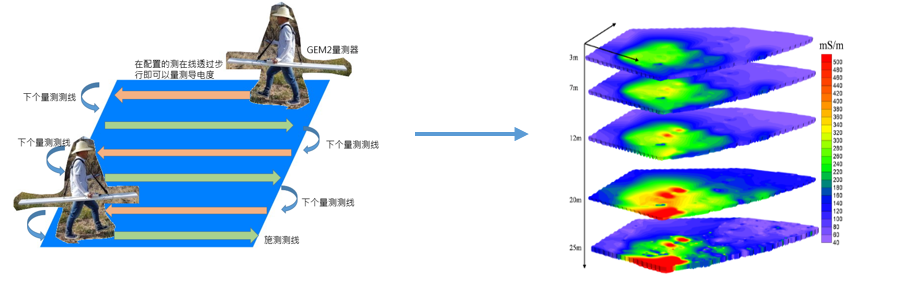
Figure 3-4 Schematic diagram of electromagnetic detection method
The main purpose of environmental geophysical methods is to increase the on-site information, from the original point information to the surface and the body, not to replace the traditional detection technology. More on-site information can better verify the accuracy and timeliness of environmental geophysical methods, which is complementary to traditional drilling and sampling.
The high-density resistivity method and the induction electromagnetic method can simultaneously provide the horizontal and vertical distribution in the survey of the garbage dump, and present the results in a graphical way to help the owner grasp the pollution distribution of the site. This scheme is expected to achieve the following purposes:
(1) Through the induction electromagnetic method, the characteristics of soil conductivity in a large range can be obtained, and the large conductivity distribution of the site can be delineated.
(2) Combined with the high-density resistivity method, information such as the vertical distribution range, boundary range and depth of the landfill can be effectively checked.
(3) Clarify the stratification of the landfill site, the depth and migration of groundwater, and delineate the dominant concentration area and migration channel of landfill leachate.